Zero water Concept (ZWC)
The ZWC is a technology which can be connected to a Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS). The ZWC reduces the water consumption even further than the core RAS.
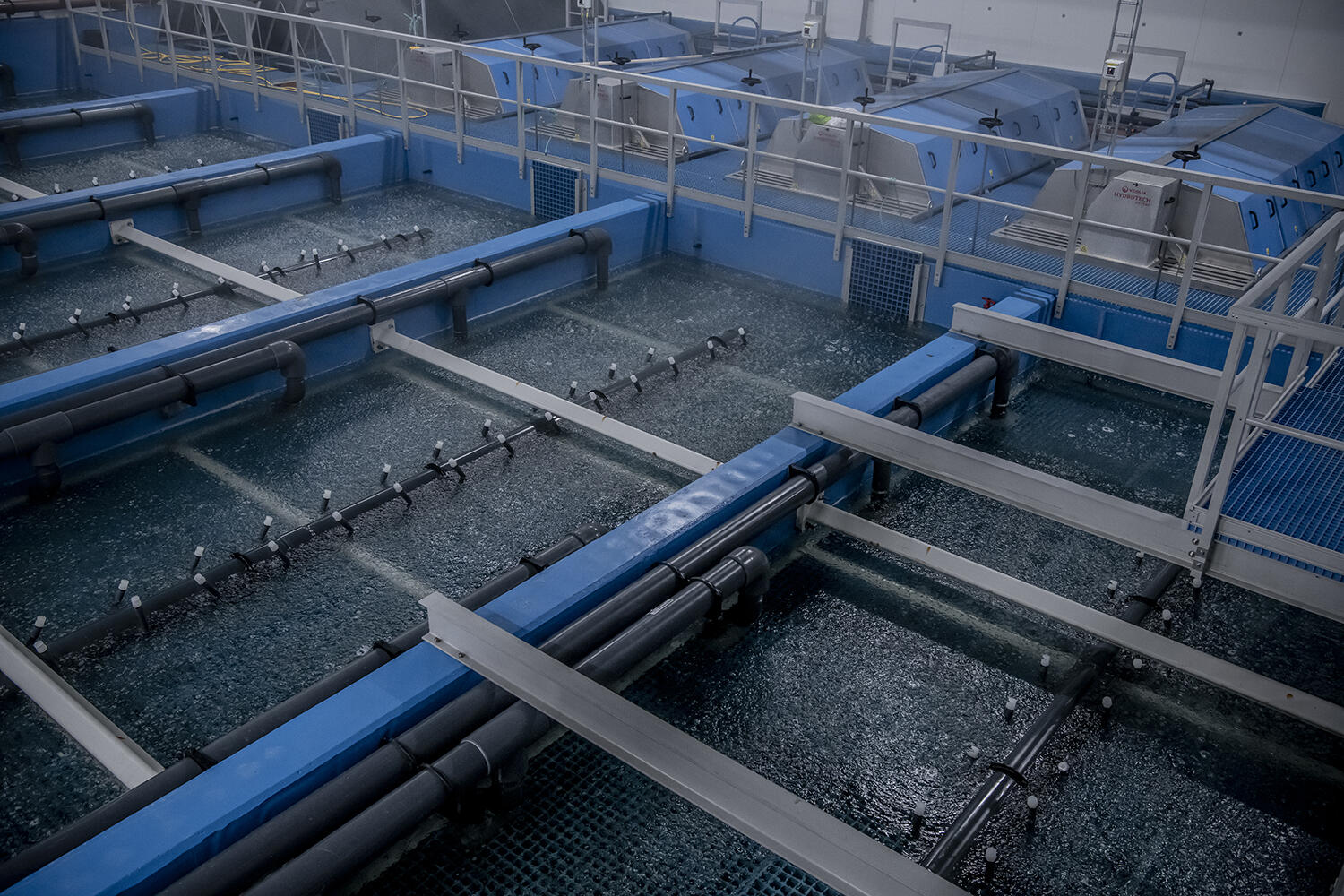

The ZWC is a technology which can be connected to a Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS). The ZWC reduces the water consumption even further than the core RAS.
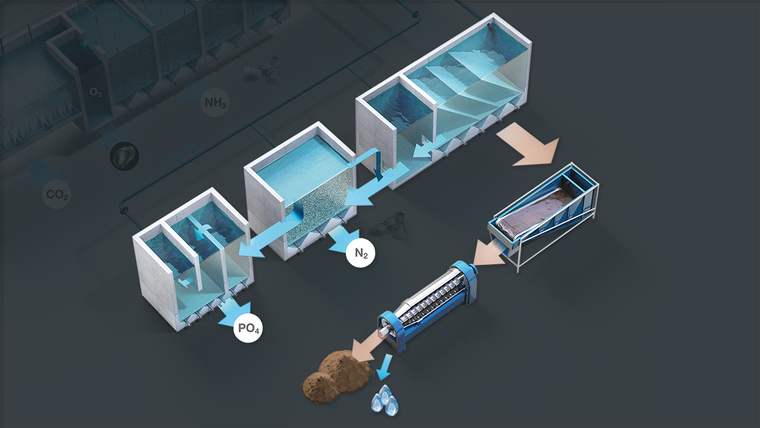
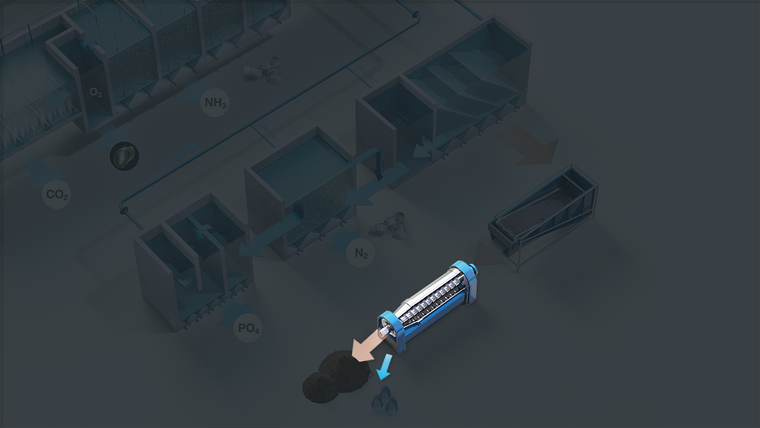
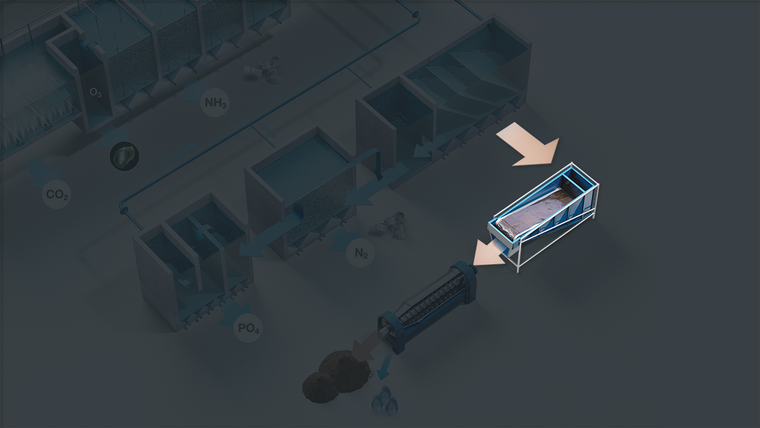
The Zero Water Concept (ZWC) significantly reduces the consumption of new water for the RAS. The technology is a 3-step sludge handling process. It works by de-nitrification of the RAS process water, converting nitrate into free nitrogen that is released in the air. The water is returned to the RAS after a step that removes phosphorus and other inorganic compounds from the process water.
The ZWC technology is used in areas with limited access to new water, or when extra treatment of the effluent water is required.
The saving of water using ZWC can be up to ten times the RAS’s water consumption, depending on the RAS’s intensity.
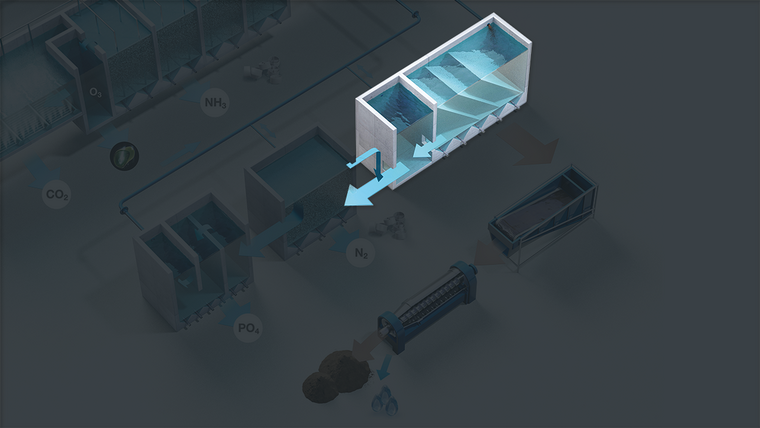
Particles in the water coming from the mechanical filter settles in the plate separator and is pumped out for external wastewater treatment (WWT). The cleaned water runs to the de-nitrification system where the remaining fine particles act as food source for nitrifying bacteria.
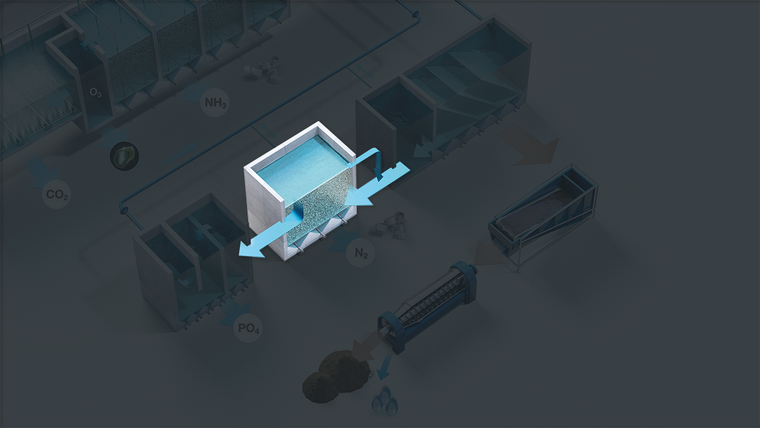

Bacteria transform nitrate into nitrogen gas by the use of a carbon source such as methanol. Increased alkalinity through this process reduces the need for adding alkalinity when compared to basic RAS
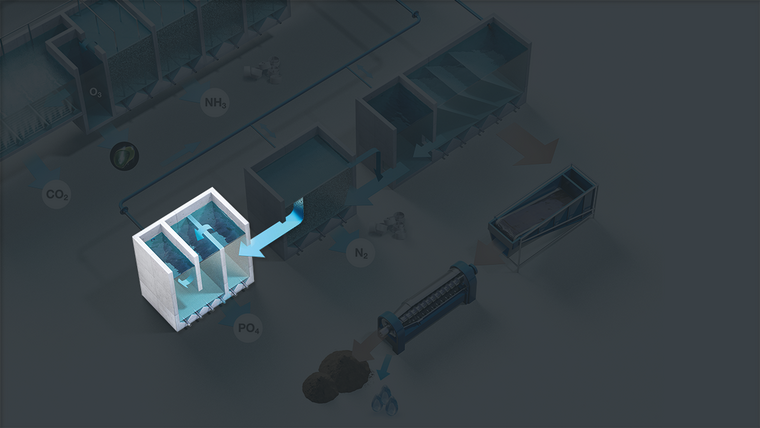

The system facilitates precipitation of dissolved phosphorous and sedimentation of fine particles and other substances that would otherwise accumulate in the system.
The beltfilter dewaters sludge coming from the ZWC plate separator to a dry matter content of around 10%. Sludge at 10% dry matter is often used for soil improvement in agriculture or a source in biogas production. A decanter centrifuge can be added to thicken the sludge up to 30% to reduce the volume of sludge. Reject water will need to be discharged according the local consent levels.